Working principle of paper cup machine
A paper cup machine is an advanced piece of manufacturing equipment designed to automatically produce paper cups used for beverages like coffee, tea, and soft drinks. These machines combine mechanical precision, heating technology, and automation to transform flat sheets of coated paper into perfectly shaped, leak-proof paper cups. Understanding its working principle provides insight into how everyday disposable cups are efficiently mass-produced with consistency and hygiene.
1. Raw Material Preparation
The main material used in a paper cup machine is PE-coated paper (polyethylene-coated paper). This special paper has a thin plastic film on one or both sides to make it waterproof and heat-resistant. The paper is usually pre-printed with brand designs and logos before being cut into small rectangular pieces called fan-shaped blanks. Another key material is the bottom roll paper, which forms the base of the cup.
2. Feeding and Shaping the Cup Body
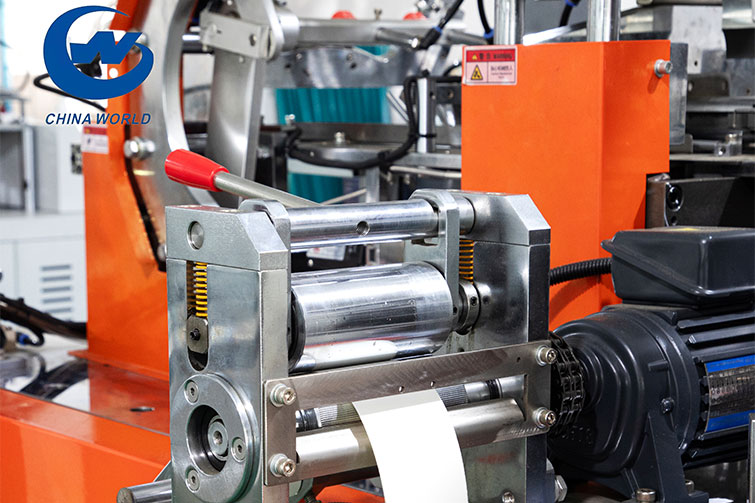
The process begins when the paper blanks are automatically fed into the machine one by one. A mechanical arm or suction device picks up each blank and inserts it into a forming mold. Inside the mold, the paper is curled into a cylindrical shape, and the vertical edges are overlapped. To make the side joint firm and leak-proof, the overlapping area is heated by a hot air system or ultrasonic sealing system, which melts the thin PE layer and bonds the edges tightly together. This forms the main body of the cup.
3. Cup Bottom Formation
After the body is shaped, the machine automatically cuts circular disks from the bottom roll paper. These disks are placed at the bottom of the cylindrical paper tube. Using precise positioning, the disk is inserted and sealed to the body by heating and pressing. This creates a complete closed structure — a cup with a bottom. The heating ensures that the PE coating melts slightly, bonding the bottom and body securely.
4. Curling and Rim Formation
Next, the upper edge of the cup is curled outward to create a smooth and strong rim. This step is crucial for user comfort and cup strength. The curling is done by rotating molds that shape the edge while applying gentle heat. The finished rim not only improves appearance but also prevents leakage and makes the cup easier to hold and fit with lids.
5. Cooling, Ejection, and Stacking
Once the cup is formed, it is cooled naturally or by air blowers. Then, a mechanical pusher ejects the finished cups from the molds and arranges them into stacks. The stacking process is carefully synchronized so that cups of the same size are neatly nested together, ready for counting and packaging. Some modern machines have automatic counters and packing systems, improving productivity and reducing manual labor.
6. Control and Automation
Modern paper cup machines are equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLC), photoelectric sensors, and servo motors to ensure precision and safety. These control systems monitor temperature, paper feeding, sealing time, and forming speed in real time. If a paper jam or misalignment occurs, the system automatically stops the machine to prevent waste or damage.
7. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Advanced models focus on energy efficiency by optimizing heating and reducing paper waste. Some machines also support biodegradable coated paper made from PLA (polylactic acid) instead of PE, aligning with global trends toward eco-friendly packaging. Manufacturers continue to develop equipment that supports sustainable materials without sacrificing quality or performance.
Conclusion
In summary, a paper cup machine transforms simple coated paper into durable, hygienic, and aesthetically pleasing cups through a series of precise mechanical and thermal processes — including feeding, shaping, sealing, curling, and stacking. Its high degree of automation allows for large-scale production with minimal human intervention. As technology advances, paper cup machines are becoming faster, smarter, and greener, playing a vital role in the modern disposable food packaging industry.